Increment and Decrement Operator in c programming
Increment and decrement operators are used in the C programming language to increase or decrease the value of a variable by 1. They are often used in loops and other control structures. Let's describe these operators using a variable x initially set to 5, and we'll use another variable y to store the result of the operations.
In C, there are two types of increment and decrement operators:
- Increment Operator in c programming
- decrement Operator in c programming
Increment Operators in c programming:
The increment operators are used to increase the value of a variable by 1. There are two forms:
- Pre-increment operator (++x): It increments x by 1 and then assigns the new value to another variable.
- Post-increment operator (x++): It first assigns the current value of x to another variable and then increments x by 1.
Example:
int x = 5;
int y;
// Pre-increment
y = ++x; // y = 6, x = 6
// Post-increment
y = x++; // y = 5, x = 6
Decrement Operators in c programming:
The decrement operators are used to decrease the value of a variable by 1. There are two forms:
- Post-decrement operator (x--): It first assigns the current value of x to another variable and then decrements x by 1.
- Pre-decrement operator (--x): It decrements x by 1 and then assigns the new value to another variable.
Example:
int x = 5; int y; // Pre-decrement y = --x; // y = 4, x = 4 // Post-decrement y = x--; // y = 5, x = 4
Graphical Representation for Increment and Decrement Operators
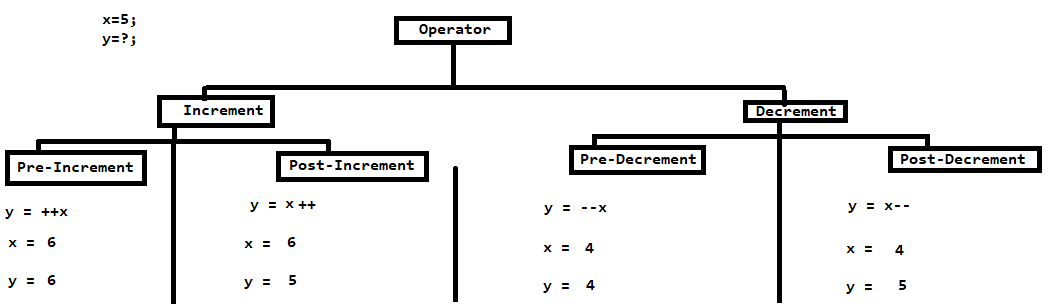
C program to demonstrate working of Unary arithmetic operators.
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a = 10, res;
// post-increment example:
// res is assigned 10 only, a is not updated yet
res = a++;
printf("a is %d and res is %d\n", a, res);
//a becomes 11 now
// post-decrement example:
// res is assigned 11 only, a is not updated yet
res = a--;
printf("a is %d and res is %d\n", a, res);
//a becomes 10 now
// pre-increment example:
// res is assigned 11 now since a is updated here itself
res = ++a;
// a and res have same values = 11
printf("a is %d and res is %d\n", a, res);
// pre-decrement example:
// res is assigned 10 only since a is updated here itself
res = --a;
// a and res have same values = 10
printf("a is %d and res is %d\n",a,res);
return 0;
}
a is 11 and res is 10 a is 10 and res is 11 a is 11 and res is 11 a is 10 and res is 10